As part of the project "Portfolio of Solutions to Strengthen Resilience Against Forest Fires: A Community and Systemic Approach for Territorial Planning and Management," funded by the Ministry of Science through the Public Challenges competition for post-forest fire recovery, native species planting sessions were carried out in the Laguna Junquillar Wetland (San Pedro de la Paz) and at Fundo Coihueco (Penco).
This project aims to evaluate resilience indicators against fires and, together with local stakeholders, select feasible and relevant solutions to strengthen preparedness for such disasters. The prioritized measures were defined considering their urgency and the interest in co-design and co-implementation by local communities.
According to Francisco de la Barrera, an academic at the University of Concepción and researcher at CEDEUS, director of the project: "The ultimate goal is to complete the full cycle to strengthen resilience against fires, assessing everything from resilience needs to implementation, thereby contributing to the transformation of territories to better face the growing threat of forest fire spread."
Solutions for San Pedro de la Paz: Green Firebreaks with Native Species
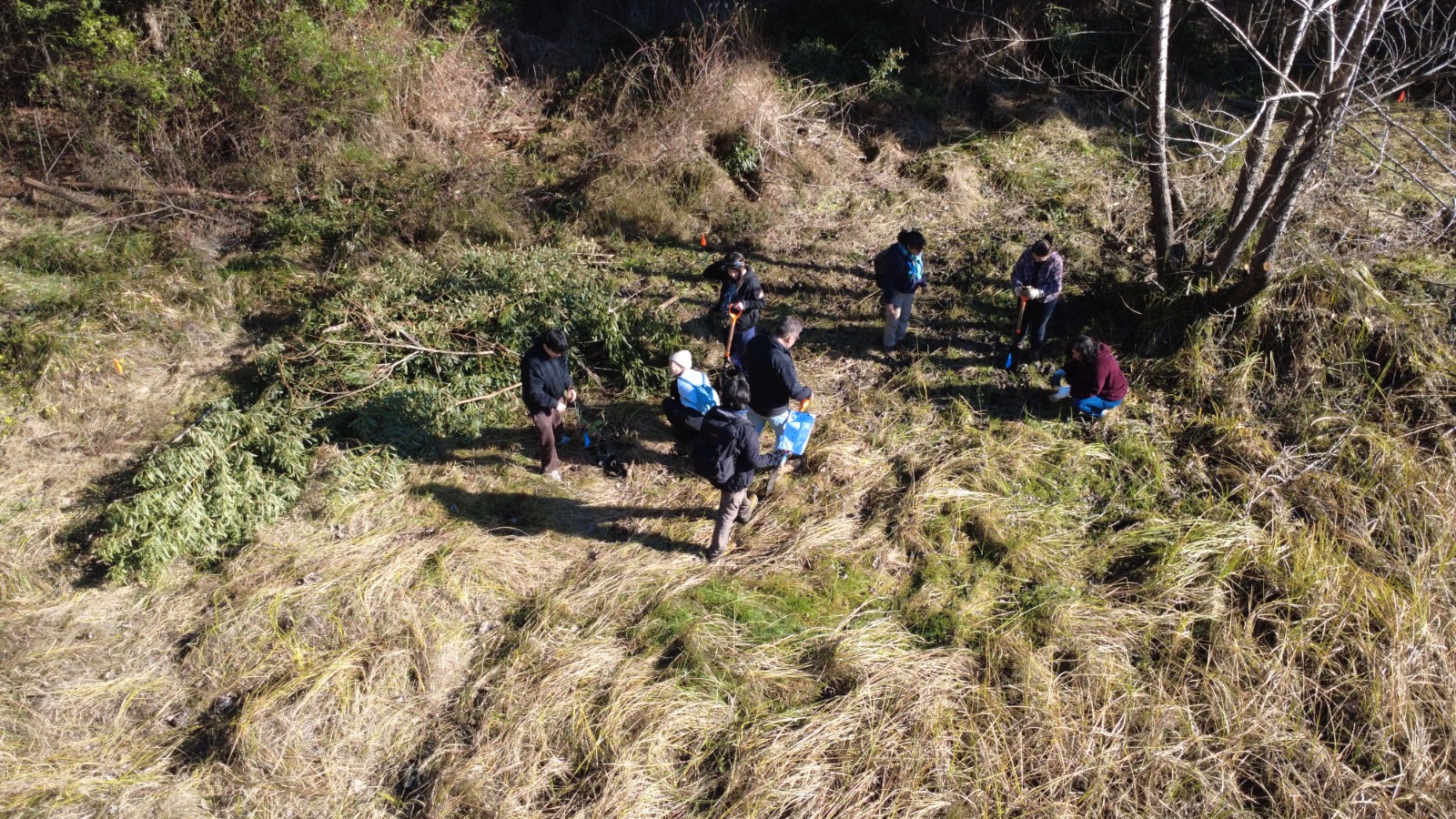
The prioritized solution for San Pedro de la Paz was the integration of native species as green firebreaks, accompanied by the clearing of exotic and flammable vegetation in an area associated with a strategic ecological corridor.
In total, 1,150 native trees and shrubs were planted, which will help strengthen resilience against fires. A significant portion of these plants were donated by the Regional Ministerial Secretariat of the Environment (Seremi de Medio Ambiente).
The activity included the participation of residents, local organizations, students, and researchers from the University of Concepción, as well as council members and professionals from the Municipality of San Pedro de la Paz, particularly from the Environmental and Sanitation & Ornament departments.
Reforestation in Penco: Protecting Water Ecosystems and Reducing Risk
In Penco, the prioritized measure was enriching an ecological corridor linked to the Penco Estero at Fundo Coihueco. The activity included planting 620 native shrubs and trees and clearing exotic vegetation to contribute to conservation while also serving as a green firebreak.
The event saw the participation of local individuals and organizations, professionals from the Communal Planning Secretariat of the Penco Municipality, and representatives from the company Arauco.
Interinstitutional and Collaborative Participation
This project is led by the University of Concepción, with the involvement of researchers, professionals, and thesis students from the institution, alongside the Pontifical Catholic University and the Austral University. It also benefits from the collaboration of key stakeholders such as the municipalities of Talcahuano, Penco, and San Pedro de la Paz, SENAPRED, MINVU, CONAF, MMA, and invited community organizations, including Corporación Junquillar and Corporación Parque Para Penco.






Comments (0)
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!
Leave a comment